Cottage cheese has quietly made a comeback. Once known as a “diet food” from decades past, it’s now showing up everywhere—from fitness meal plans to viral recipes on social media. And honestly? It deserves the attention.
When you look closely at cottage cheese nutrition facts, you realize this simple dairy food packs way more value than most people expect. It’s high in protein, versatile, and surprisingly filling. But it’s not perfect for everyone, and not all cottage cheese is created equal.
This guide breaks everything down in plain, everyday language—so you can decide if cottage cheese actually fits your lifestyle.
What Is Cottage Cheese, Exactly?
Cottage cheese is a fresh cheese made from curds of cow’s milk. Unlike aged cheeses, it’s not pressed or ripened. That’s why it has a soft, lumpy texture and a mild, slightly tangy taste.
It’s typically sold in:
- Full-fat
- Low-fat
- Fat-free versions
You’ll also see small-curd and large-curd varieties. Nutritionally, they’re very similar.
Cottage Cheese Nutrition Facts (Per 1 Cup, Low-Fat)
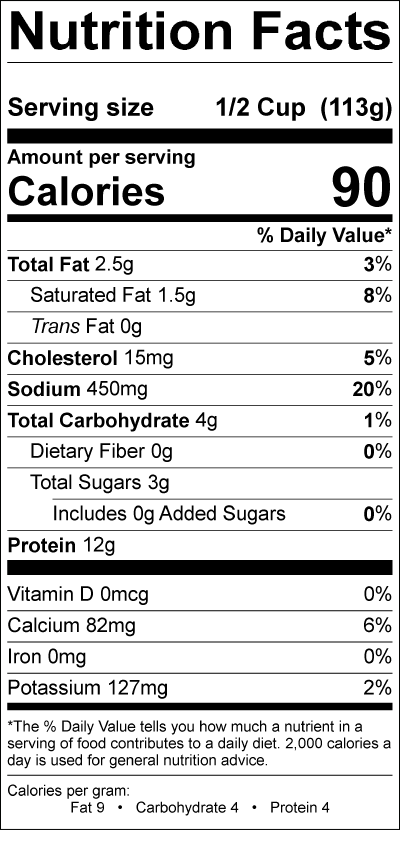
Here’s what you get in one cup (about 226 grams) of low-fat cottage cheese:
- Calories: ~180
- Protein: ~24–28 grams
- Fat: ~5 grams
- Carbohydrates: ~6 grams
- Sugar (natural lactose): ~4 grams
- Calcium: ~140 mg
- Sodium: ~700 mg
Right away, one thing stands out: protein.
Cottage cheese delivers more protein per calorie than many other dairy products.
Why Cottage Cheese Is So High in Protein
Casein Protein Explained
Most of the protein in cottage cheese comes from casein, a slow-digesting protein. That’s a big reason it keeps you full longer than yogurt or milk.
This makes cottage cheese especially useful for:
- Muscle repair
- Appetite control
- Evening snacks (it digests slowly overnight)
Fitness-focused resources like Healthline often highlight cottage cheese as a smart protein source for both active and everyday people.
The Amino Acids Most People Miss
Cottage cheese contains all nine essential amino acids. These are the building blocks your body can’t make on its own.
One key amino acid is leucine, which plays a major role in muscle maintenance. That’s why cottage cheese is popular with athletes and older adults alike.
Calcium: More Than Just Bones
Yes, cottage cheese provides calcium—but its role goes beyond bone health.
Calcium also supports:
- Muscle contraction
- Nerve signaling
- Hormone release
If you’re browsing dairy foods alphabetically, cottage cheese earns its spot on our foods that start with C list for good reason.
Sodium: The One Nutrition Fact to Watch
This is where cottage cheese can surprise people.
Why Sodium Is Higher
Salt is added during the curd-forming process. That boosts flavor but also raises sodium levels.
For most healthy adults, this isn’t a deal-breaker. But if you’re managing blood pressure, look for:
- “Low sodium” cottage cheese
- Rinsed curds (some brands offer this)
The American Heart Association recommends keeping sodium intake in check, especially if you eat processed foods regularly.
Cottage Cheese vs Yogurt: Which Is Better?
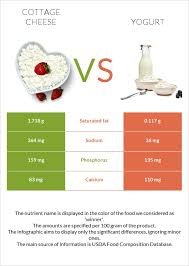
Both are nutritious, but they serve different purposes.
Cottage Cheese
- Higher protein
- Lower sugar
- More filling
Yogurt
- Contains probiotics
- Creamier texture
- Often higher in sugar (especially flavored)
If protein is your main goal, cottage cheese usually wins. If gut health is your priority, yogurt may be the better choice.
Fat Content: Does It Matter?
Cottage cheese comes in several fat levels, and none are “bad” by default.
Full-Fat Cottage Cheese
- More satisfying
- Better flavor
- Slightly higher calories
Low-Fat or Fat-Free
- Lower calories
- Higher protein-to-calorie ratio
- Can feel less filling for some people
The best choice depends on your overall diet, not just the label.
Is Cottage Cheese Good for Weight Loss?
Cottage cheese can be helpful for weight management because it:
- Promotes fullness
- Helps preserve muscle
- Is easy to portion
According to research summarized by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, high-protein foods support appetite control when combined with balanced eating habits.
That said, cottage cheese isn’t a magic food. It works best when paired with fiber-rich foods like fruit, vegetables, or whole grains.
Lactose: Can Everyone Eat Cottage Cheese?
Cottage cheese contains lactose, but less than milk.
Many people who struggle with milk can still tolerate cottage cheese in moderate amounts. However, those with severe lactose intolerance may still experience discomfort.
Lactose-free cottage cheese options are becoming more available and are worth exploring.
Best Ways to Eat Cottage Cheese (That Aren’t Boring)

Cottage cheese has come a long way from plain bowls with pepper.
Try it:
- With berries and honey
- Blended smooth and used as a dip
- On toast with avocado
- Mixed into scrambled eggs
- Paired with tomatoes and olive oil
Cottage Cheese for Different Diets
High-Protein Diets
Excellent fit due to casein protein.
Low-Carb Diets
Naturally low in carbs.
Vegetarian Diets
Strong protein source without meat.
Keto Diets
Full-fat versions work better than low-fat.
Does Cottage Cheese Expire Quickly?
Yes. Cottage cheese is a fresh product.
Always:
- Keep it refrigerated
- Use clean utensils
- Follow the “use by” date
If it smells sour or develops mold, discard it.
Common Questions About Cottage Cheese Nutrition Facts (FAQ)
Is cottage cheese healthier than cheese slices?
In most cases, yes. It’s lower in fat and higher in protein.
Can you eat cottage cheese every day?
Yes, for most people, as part of a balanced diet.
Is cottage cheese good before bed?
Yes. Casein protein digests slowly, which may support muscle repair overnight.
Is cottage cheese processed?
It’s minimally processed compared to many packaged foods.
Does cottage cheese spike blood sugar?
It’s low on the glycemic scale and generally blood-sugar friendly.
The Bottom Line
When you really look at cottage cheese nutrition facts, it’s easy to see why this food keeps coming back into the spotlight.
It’s simple. It’s affordable. And it delivers serious nutrition without much effort.
The key is choosing the right version for your needs and enjoying it in ways that actually taste good to you.
Cottage cheese doesn’t need a rebrand. It just needs a fair look.
Our Authority Sources
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health – Dairy & Protein Research
- American Heart Association – Sodium and Heart Health
- Healthline – Cottage Cheese Nutrition Overview
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Calcium Fact Sheet

